 Image by K.T.J. Davies
Image by K.T.J. Davies
Abstract
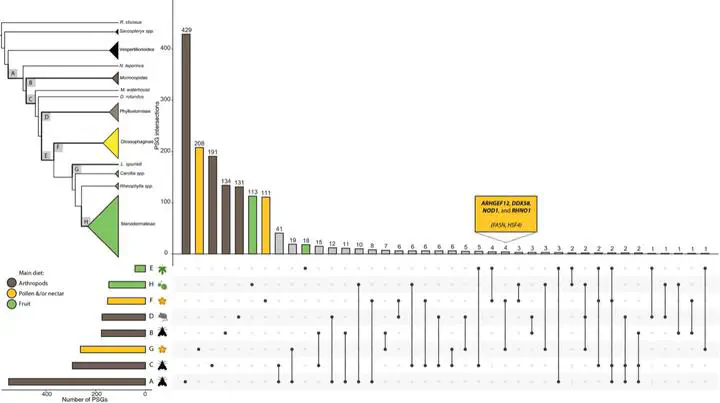
Changes in behaviour may initiate shifts to new adaptive zones, with physical adap- tations for novel environments evolving later. While new mutations are commonly considered engines of adaptive change, sensory evolution enabling access to new resources might also arise from standing genetic diversity, and even gene loss. We examine the relative contribution of molecular adaptations, measured by positive and relaxed selection, acting on eye-expressed genes associated with shifts to new adaptive zones in ecologically diverse bats from the superfamily Noctilionoidea. Collectively, noctilionoids display remarkable ecological breadth, from highly diver- gent echolocation to flight strategies linked to specialized insectivory, the parallel evolution of diverse plant-based diets (e.g., nectar, pollen and fruit) from ancestral insectivory, and—unusually for echolocating bats—often have large, well-developed eyes. We report contrasting levels of positive selection in genes associated with the development, maintenance and scope of visual function, tracing back to the origins of noctilionoids and Phyllostomidae (the bat family with most dietary diversity), instead of during shifts to novel diets. Generalized plant visiting was not associated with exceptional molecular adaptation, and exploration of these novel niches took place in an ancestral phyllostomid genetic background. In contrast, evidence for positive selection in vision genes was found at subsequent shifts to either nectarivory or frugivory. Thus, neotropical noctilionoids that use visual cues for identifying food and roosts, as well as for orientation, were effectively preadapted, with subsequent molecular adaptations in nectar-feeding lineages and the subfamily Stenodermatinae of fig-eating bats fine-tuning pre-existing visual adaptations for specialized purposes.