Dynamic metabolic and molecular changes during seasonal shrinking in Sorex araneus
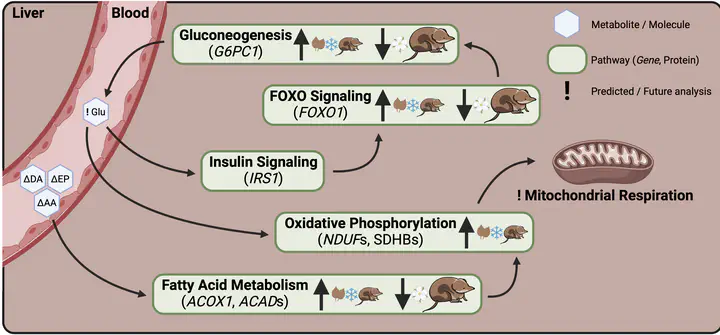 Image credit: W.R. Thomas
Image credit: W.R. Thomas
Abstract
To meet the challenge of wintering in place many high-latitude small mammals reduce energy demands through hibernation. In contrast, short-lived Eurasian common shrews, Sorex araneus, remain active and shrink, including energy-intensive organs in winter, regrowing in spring in an evolved strategy called Dehnel’s phenomenon. How this size change is linked to metabolic and regulatory changes to sustain their high metabolism is unknown. We analyzed metabolic, proteomic, and gene expression profiles spanning the entirety of Dehnel’s seasonal cycle in wild shrews. We show regulatory changes to oxidative phosphorylation and increased fatty acid metabolism during autumn-to-winter shrinkage, as previously found in hibernating species. But in shrews we also found upregulated winter expression of genes involved in gluconeogenesis: the biosynthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates. Co-expression models revealed changes in size and metabolic gene expression interconnect via FOXO signaling, whose overexpression reduces size and extends lifespan in many model organisms. We propose that while shifts in gluconeogenesis meet the challenge posed by high metabolic rate and active winter lifestyle, FOXO signaling is central to Dehnel’s phenomenon, with spring downregulation limiting lifespan in these shrews.